Form factor
Contents |
[edit] General
Form factor, it could be said in general is a mathematical way to compare two different variables of an object by ratios. It is commonly used in the electronic hardware industry ascwell as the design and construction industry.
[edit] Electronics
In electronics form factor might be used in different ways to describe the size, shape, and specification of various pieces of hardware or components such as motherboards, USB and disc drives or memory cards.
[edit] Buildings
In the design and construction of buildings, form factor is a simplified way of measuring the efficiency of a buildings' shape, by means of a ratio between the external surface area (SA) and the internal treated floor area (TFA). This is specifically useful when it comes to heating, because the TFA is the floor area to be heated and the SA is the surface through which the heat will gradually be lost. The lower the ratio between the two the slower will be the heat loss for the same level of fabric performance.
Lower heat loss factors ( or ratios) of between 0.7 and 2.0 will be found with simple medium to high rise buildings whilst higher factors from 2.0 up to 5.0 will be found wih lower rise and single detatched dwellings as these have a greater surface area that is exposed to the outside.
[edit] Passivhaus
Form factor has gained interest, partly because it is a fundamental element of the internationally recognised passivhaus standard. This is a design and construction standard for passive buildings which targets achieving thermal comfort only by the heat generated by the occupants ( or minimal heating) , it does so though super insulation, minimising thermal bridges, airtightness, triple glazed openings, and ventilation systems with heat recovery.
[edit] Detail
Form factor is a simplification tool and designers should be aware that there are some complexities in the different ways certain variables are calculated when it comes to the detail. For example in the passivhaus air tightness test (n50) the treated floor area used to calculate the internal volume excludes any internal walls and floors. In the infiltration air change rate used for ATTMA & Buildings Regulations, it is the number of cubic meters of air leakage per hour per metre 2 of the envelope that is of concern. As such intermal walls and floors are included as within the total internal volume as the variable considered. ith Passive hoause being measured as ≤ 0.6 h-1@ 50 Pa. and ATTMA as m3/hr/m2@50Pa (q50).
for further information visit the passivhaustrust or the ATTMA.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Exchange for Change for UK deposit return scheme
The UK Deposit Management Organisation established to deliver Deposit Return Scheme unveils trading name.
A guide to integrating heat pumps
As the Future Homes Standard approaches Future Homes Hub publishes hints and tips for Architects and Architectural Technologists.
BSR as a standalone body; statements, key roles, context
Statements from key figures in key and changing roles.
ECA launches Welsh Election Manifesto
ECA calls on political parties 100 day milestone to the Senedd elections.
Resident engagement as the key to successful retrofits
Retrofit is about people, not just buildings, from early starts to beyond handover.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
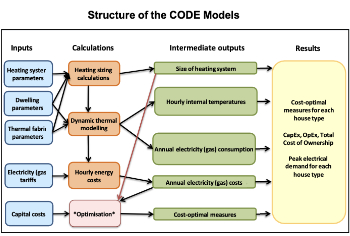
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.



















Comments
The definition of form factor shown in this article is incorrect. The form factor relating to heat loss is the ratio of the total heat loss envelop area to the total heated floor area (not the other way round as described in the article).
Thankyou, I believe you are correct, as we are a wiki please feel free to edit the page yourself and we will review also but thankyou for the comment. Best the editor.