WiFi definition
WiFi technology (IEEE802.11) can be broadly categorised to IEEE802.11 a/b/g/n/ac. Each is an improvement in transmission speed and/or signal range from the previous, although these days only ‘G’ and ‘N’ are used.
The standard G versions of networking devices have an optimal transmission speed of 54 Mbps with an indoor range of approximately 40 m whereas the N versions have a theoretical maximum speed of 300 Mbps (practical of approximately 150 Mbps and above) with an indoor range in the region of 70 m.
In addition to this, N variations offer the choice of two frequency ranges; 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz. The higher frequency has no impact on the range but offers a potentially less polluted frequency to help reduce crosstalk noise.
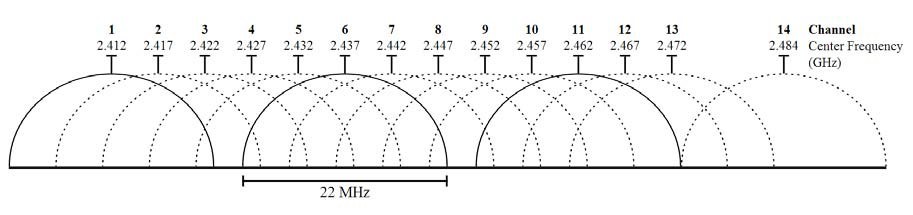
Both the G and the N devices utilise the same channel capabilities but these vary regionally. In Europe (including UK) a channel system of 1-13 is used whereas in the US the system uses 1-11. Both use the same frequency ranges resulting in an approximate frequency void of 16.5 MHz at the end of the 2.4 GHz range.
Japan utilise a different system still, expanding the 2.4 GHz range beyond the acceptable ISM guidelines by 10.5 MHz to allow for an additional 14th channel with 11 MHz of non-interference from other channels (see Figure below) [80], [81], [82].
Image. 22MHz channel allocations for WiFi 2.4GHz frequencies, with curvatures implying affinities for intra-channel frequency selection.
The figure above shows the affinities for the frequency selection within each 22 MHz channel and the overlap between channel frequencies. The same would be seen for 40 MHz channels with the obvious exception that there would be twice the amount of overlap between channels, leaving fewer isolated channels. The solid lines show the 3 channels in the US 11 channel system that do not encroach on each other’s range at all. Each WiFi access point will secure its own channel and use that channel for all communications. Multiple channels will not be utilised by one access point other than during overlap.
WiFi communication protocols are Internet Protocol (IP) based where the destination address is in packet headers allowing large amounts of data to be transmitted through a network of nodes at high speed. This means that on any WiFi network a central control node (network coordinator) will allocate all IP’s in the network on discovery allowing for any packets to be addressed and routed to a connected device [82].
This article was created by --BRE. It was taken from The future of electricity in domestic buildings, a review, by Andrew Williams, published in November 2014.
NB The term 'WiFi' was coined by the Wi-Fi Alliance as shorthand for wireless local area network (WLAN) products based on the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers' (IEEE) 802.11 standards. It did not specifically 'stand for' anything. It has popularly been adopted to mean Wireless Fidelity but this is not correct.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Bluetooth.
- CAT5.
- Ethernet
- Extranet
- Glossary of electrical terms.
- ICT and Automation (ICTA) Scoping Study Report.
- In-building wireless.
- Information and communications technology.
- Internet of things.
- Internet of things in commercial buildings.
- Local area network.
- Smart buildings.
- Smart cities.
- Smart technology.
- The future of electricity in domestic buildings.
- WiMax.
- WiredScore.
- ZigBee.
[edit] External references
- [80] E. G. Villegas, E. López-Aguilera, R. Vidal and J. Paradells. Effect of adjacent-channel interference in IEEE 802.11 WLANs. Cognitive Radio Oriented Wireless Networks and Communications, Orlando, 2007.
- [81] Butler J. Wireless Networking in the Developing World, Copenhagen: Creative Commons, 2013.
- [82] Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. IEEE Standards, 2012.
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.


























Comments
WiFi does not stand for Wireless Fidelity. It is not an acronym. It is a term to define the ieee 802.11 standard.
WiFi was coined by the Wi-Fi Alliance as shorthand for wireless local area network (WLAN) products based on the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers' (IEEE) 802.11 standards. It did not specifically 'stand for' anything. It has popularly been adopted to mean Wireless Fidelity but this is not correct.