Microchip
|
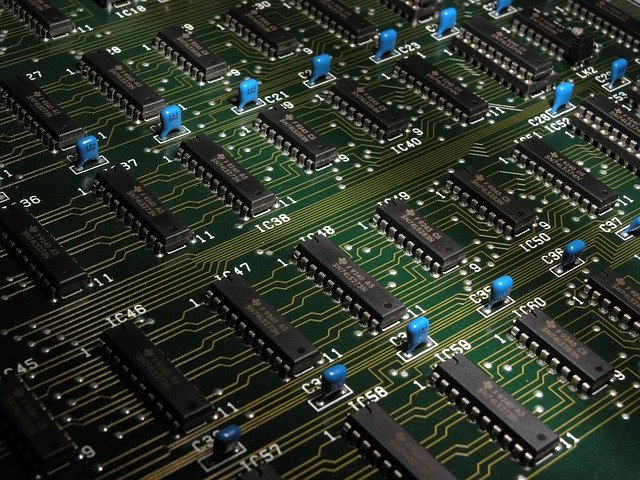
A microchip (also called a chip, integrated circuit or IC) comprises a series of electronic circuits on a small chip or semiconductor material that is typically made of silicon. It has almost completely replaced the use of the bulkier transistor and can be seen in the entire spectrum of electronic devices, including computers, mobile phones, TVs and radios, and a host of other domestic and industrial appliances.
Before the microchip, electronic components were huge: valves the size of domestic light bulbs and bigger. One of the first computers used by mathematician and codebreaker Alan Turing took up half a small room. The fact that today electronics can be compressed to the micro scale is largely due to the advent first of the transistor and more recently the microchip.
Traditionally, all the components of an electric circuit were placed on a board and joined together by wires or soldering. This created a very large, bulky circuit which resulted in correspondingly large appliances, whether radios, TV sets or computers.
In order to try and miniaturise the entire circuit, US-based electrical engineer Jack Kilby had the idea of replacing all the circuit components with a single material. He then hit on the idea of using a semi-conductor such as silicon which could act as required in various ways – either as a conductor of electricity or as an insulator.
Working at Texas Instruments in May 1958, Kilby experimented with slithers of silicon to create integrated circuits in which all the components were not conventional, single, freestanding entities but integrated into a whole. In the process, he invented the first monolithic integrated circuit – or microchip. In February 1959, he applied for a patent which was eventually granted five years later.
As with numerous other inventions where two inventors working independently claim to be the originators of an idea, another patent application for a very similar type of microchip was put in by Robert Noyce in 1959, very shortly after Kilby’s application. However, Kilby is regarded as the true inventor although some sources also credit Noyce.
Since Kilby’s invention, technical advances in the manufacture of metal-oxide-silicon (MOS) semiconductors have resulted in ever-increasing miniaturisation, accompanied by larger capacity chips working at much faster speeds. Modern microchips can have billions of MOS transistors in an area the size of a one-penny coin. The result is that today’s computer chips have capacities that are a million times greater and thousands of times faster than chips of the early 1970s.
Kilby went on to invent the first hand-held electronic calculator (1972) and became co-founder of Intel. He died in 1990 at the age of 62. In 2000, he was posthumously awarded the Nobel Prize for physics.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.

























