Better prediction of overheating in new homes
A detailed study of three modern, energy-efficient flats has been carried out to improve the means of predicting indoor temperatures and the risk of overheating, when designing multi-residential buildings.
Overheating in modern homes – which are often designed with a focus on improving energy efficiency – is a growing problem and likely to be exacerbated by climate change. To counter this, it is important when designing buildings to reliably assess indoor temperatures and the potential for overheating. These are typically predicted with dynamic simulations, using Building Performance Simulation (BPS) tools.
BPS tools need accurate data on a complex range of issues in the areas of climate, site context, building fabric, building services and occupant behaviour. All of these bring high levels of uncertainty that make correctly predicting indoor temperature very difficult, and can lead to a gap between the expected and actual performance.
A BRE Trust supported PhD project has been conducted by Kostas Mourkos at Loughborough University, to improve BPS tools’ reliability when predicting overheating risks in homes in multi-residential buildings. This was achieved by studying in detail three modern energy-efficient flats located in London. The flats are representative of many high-density developments built in London in recent years.
Areas of overheating assessments that have been revealed as needing improvement by the analysis include:
- Specifying input values for parameters, such as the ventilation rates of mechanical ventilation systems.
- Providing guidance on handling the thermal interaction between communal spaces and the assessed flat.
- Examining different infiltration and exfiltration pathways.
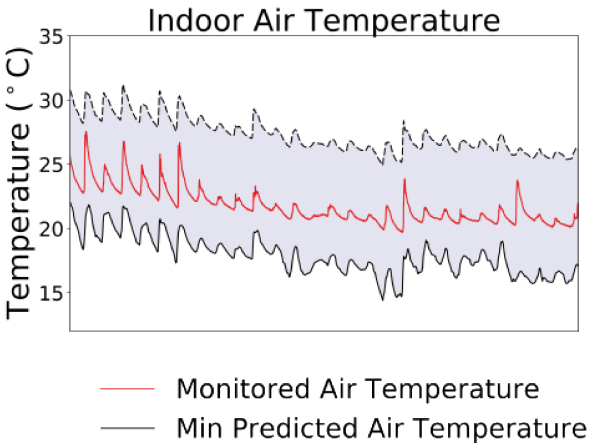
The analysis also identified the key parameters influencing the observed gap between predicted and monitored indoor air temperature. While demonstrating how such a gap can be efficiently bridged through Bayesian calibration, this research showed that predicting overheating accurately remains challenging.
The research recommended that an overheating assessment should incorporate sources of uncertainty (such as occupant behaviour), by providing a range of values – instead of a single value – of the desired Building Performance Indicator (BPI). It should also consider using less sensitive overheating metrics.
Kostas was supervised by Prof Christina Hopfe and Dr Rob McLeod at Graz University of Technology, Dr Chris Goodier at Loughborough University, and Dr Mick Swainson at BRE. For more information contact Kostas ([email protected]) or access the paper.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- BRE articles.
- BRE Trust.
- Building Research Establishment.
- Heat stress.
- Home Quality Mark high temperature reporting tool.
- Human comfort in buildings.
- Overheating - assessment protocol.
- Overheating in residential properties.
- Overheating.
- Preventing overheating.
- Solar gain.
- Thermal comfort.
- Thermal indices.
- Thermal pleasure in the built environment.
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.