Elastic limit
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
All materials show elastic behaviour to a degree, some more than others. If, after a load has been applied and then quickly removed, a material returns rapidly to its original shape, it is said to be behaving elastically. Elasticity is a crucial characteristic of building materials; if it were not, buildings would suffer continuous deformation under load and ultimately would collapse.
[edit] Elastic limit
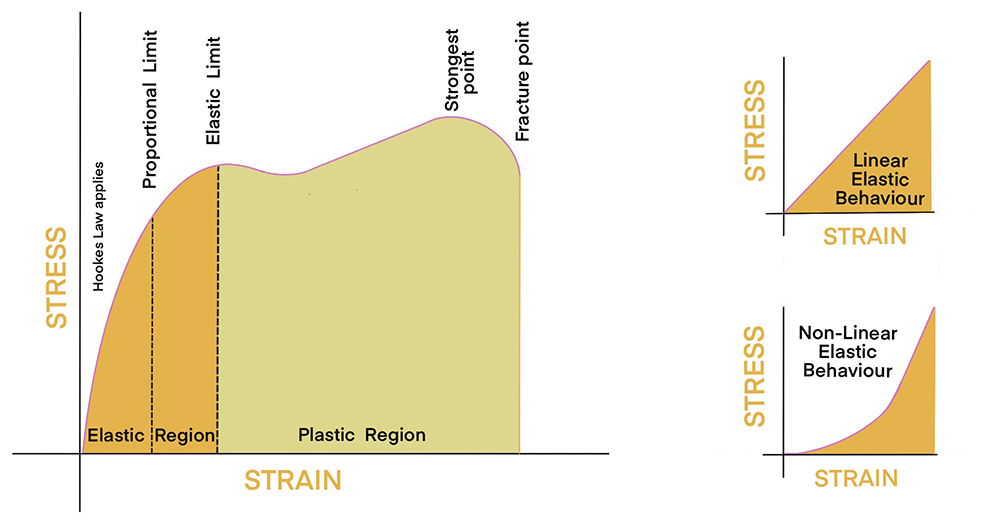
A solid material’s elastic limit is the maximum stress per unit area it can withstand before there is permanent deformation. In other words, it is the limit of the material’s elasticity, for up to that point, the solid can resume its original shape when the load is removed; after that point, it undergoes permanent (plastic) deformation and will not return to its original shape even after the load (yield load) has been removed.
On a graph showing a stress-strain curve, the point of the limit of elastic behaviour is called the ‘yield point’ and this is where plastic deformation begins – some of this deformation will be plastic and irreversible. In structural engineering, the yield point is regarded as a ‘soft failure’ mode which does not usually cause catastrophic or ultimate failure. It might be referred to as the fracture point or in the case of structural failure the breaking point, such as where a timber beam goes beyond, the yield, soft failure and fracture to break and collapse.
No structural material exhibits perfect elasticity: depending on the type of structure and the material, permanent deformations are unavoidable whenever loads exceed certain values. That is why engineers design structures to ensure the materials are being used within their elastic range and the loads involved will not produce permanent deformations.
All structural materials behave plastically beyond their elastic range. However, even if some materials show elastic behaviour, they may – after a long period of service, usually many years – exhibit a degree of plastic flow (or creep).
[edit] Linear elasticity
This occurs when the deformation in a material is proportional to the load applied. So, if a person weighing 50kg causes a diving board to deflect by 300mm, and another person weighing 100kg causes an identical board to deflect by 600mm, the diving board is exhibiting linear deflection. Most structural materials are, within limits, linearly elastic and are used within their linearly elastic range.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Concept structural design.
- Detailed design.
- Elements of structure in buildings.
- Moment.
- Stiffness.
- Structural engineer.
- Structural principles.
- Structural systems for offices.
- Structural vibration.
- Structures at the end of their design life.
- The development of structural membranes.
- Types of structural load.
- Vibrations.
Featured articles and news
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherit assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.