Dishwasher
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
A dishwasher is an appliance that uses very hot water and specialist detergent to clean dishes, glassware, cutlery and other kitchen items. There are consumer and commercial machines available, which perform the same function, but with differences in capacity and temperature.
[edit] History
The earliest version of a mechanical dishwasher was patented in the United States in 1850. The inventor, Joel Houghton, referred to the device as a machine for cleaning crockery or other types of table furniture. This device included a cylinder with a rack to hold the items being washed. A hand crank made the rack move while water splashed onto the items as they rotated in the machine.
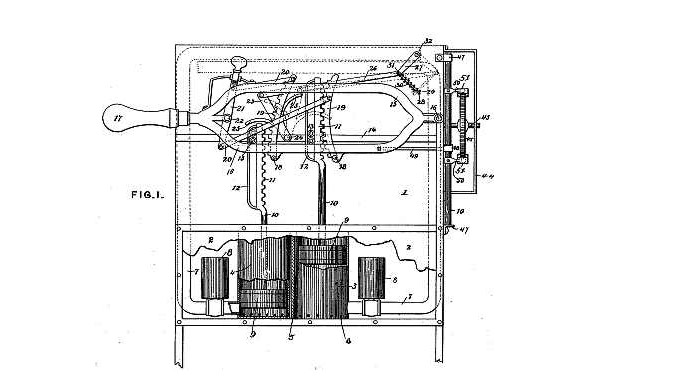
The next iteration was introduced in 1886 by Josephine Cochran (a wealthy socialite) and George Butters (a mechanic). The rack and water jet system they devised was also hand powered and was displayed to the public at the 1893 Chicago World’s Fair. The invention from the Garis-Cochran Company (later to become part of KitchenAid) garnered much attention, particularly from commercial organisations, and it was awarded the highest prize at the fair for "best mechanical construction, durability and adaptation to its line of work".
Patent serial No. 187,276 submitted by Cochran on 31 December 31 1885.
In 1924, William Howard Livens from the UK invented a non-electric dishwasher for consumer use. This machine incorporated many of the features found in modern machines, but was not widely adopted.
In 1929, Miele invented the first consumer dishwasher operated by an electric motor. However, it wasn’t until the 1950s that consumers began to see the benefits of this device, which had been thought of as a luxury up until that point. These devices were portable and independent, and some had to be manually hooked up to a sink when in use. Eventually, consumer kitchens adopted continuous countertops and uniform cabinets, so dishwashers could be integrated into the layout.
[edit] How dishwashers work
Most dishwashers operate by following the same basic steps:
- Water is added and heated. Most commercial machines use water heated to temperatures of 65–71°C while sanitation occurs at an 82°C "final rinse" temperature or through the use of a chemical sanitiser. Consumer dishwashers commonly use 75°C water, although some operate effectively with advanced detergents and lower temperatures (50–55°C). The temperatures are lower for consumer models to prevent the risk of accidental scalding.
- The detergent dispenser opens and water is sprayed at the items to be cleaned.
- Used water is drained.
- Items are rinsed with fresh water.
- Used water is drained.
- Air is heated to dry the items (commercial machines may use a different, faster method).
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.