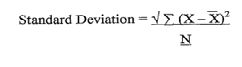Construction dissertation guide part 5 - Analysis and preparation of the results
This is part of a series of Construction Dissertation Guides for students. Click here for the whole series.
Once the data has been accumulated, the next stage is carry out analysis and present the results in a useful format.
Measurement is a procedure in which the researcher assigns numerals (numbers or other symbols) to empirical properties (variables). There are four principle levels of measurement and the primary data collection should use one or more of these.
Contents |
[edit] Nominal measurement
Nominal measurement consists of assigning items to groups or categories.
Nominal numbering implies belonging to a classification or having a particular property and a label. Since no quantitative information is expressed and there is no implied ordering of the items, nominal scales are qualitative in nature. The nominal scale is often used purely to provide an idea of quantities, for example:
- Number of lawyer-mediators from the sample = 15
- Number of construction lawyers from the sample = 6
- Number of respondents with 10+ years’ experience = 32
[edit] Ordinal measurement
Ordinal measurement is the ranking or rating of data which normally uses integers in ascending or descending order. The ordinal scale is most commonly used for calibrating the results of questionnaires that consist of attitudinal questions (that is, the recipient’s attitude towards a statement presented to them).
[edit] Alternative measurements
There are two alternative forms of measurement that can be used. The Interval Scale is used where the distance between each set of observations/data is constant, e.g. minutes, kilograms. This form of scale achieves best results when dealing with large numbers.
The Ratio Scale follows a similar concept; however, it involves a numerical scale which features a ‘natural zero’ such as age or distance.
[edit] Analysing the results
Once the data has been collected and sorted, the next stage is the analysis of those results. This is a means of determining the direction of the study and subsequently drawing conclusions in relation to the original hypothesis.
[edit] Descriptive statistics model
This can be used as a means of providing a general overview of the collected results. It is useful for questionnaire data providing results mostly in percentage or actual numerical form.
The three terms available for describing the aspects of group data are - frequency distribution, measurement of central tendency, and measurement of dispersion.
[edit] Frequency distribution
This is an assessment of the frequency of observations of each response to each variable under investigation in order to discern and display any distribution trend in the results. Results can be complex, but it is possible to represent them in a simplified way through tabulation, bar charts, pie charts or graphs.
[edit] Measures of central tendency
This is suitable where the most typical value is sought from a field of data. This can be achieved through using the mean, median and mode. The mean being the average of all the values in a set of data; the median being the value in the middle of the organised data; and the mode being the most frequently-occurring number in a set of values.
[edit] Measurement of dispersion based on the mean
This type of measurement displays the extent to which numerical information tends to be dispersed about an average value.
This can be represented by the Mean Deviation formula or, more commonly, the Standard Deviation formula:
This can be presented on a graph, where, typically, a ‘bell-like’ curve represents the data distribution.
[edit] Appraisal of the methodology
The methodology is the most important aspect of a research project, determining the overall success or failure of the study. A well-balanced collection of quality research and data is required in order to generate conclusions that may be reached and recommendations made. It is essential to carefully assess each aspect of the methodology and consider the risk of any errors that could have affected the reliability of the project as a whole.
Continue to next stage: Structuring and writing.
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.