Light shelf
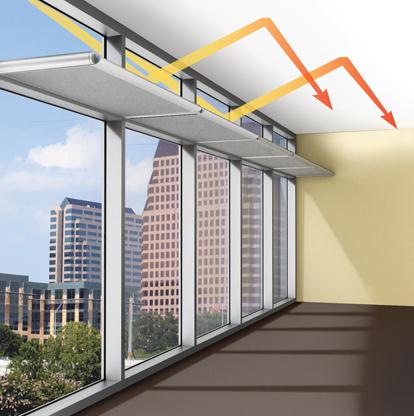
A light shelf is a passive architectural device used to reflect natural daylight into a building. 'Bouncing' sunlight off a horizontal surface distributes it more evenly and deeply within a space, whereas direct sunlight can cause glare near an opening, whilst leaving dark areas further in.
Light shelves can be fixed either externally, internally or both (which often works best in providing an even illumination gradient). They are often designed as part of a broader daylight and shading strategy.
They are generally found on walls facing the sun, as on 'pole-facing walls' would tend to act only as sunshades. On east and west orientations, they may act as an effective means of reducing direct heat gain and glare but will not bounce light as deeply into the space.
Exterior light shelves can be more effective than internal light shelves as they do not radiate as much heat into the space and so can help reduce solar heat gain and cooling loads.
Internal light shelves however may be easier to maintain as they can be more accessible and less exposed. In very broad terms, internal light shelves tend to have a depth similar to the height of the opening that they sit below.
Light shelves are commonly made from; timber, glass, plastics, metal panels, plaster, acoustic panels and so on. The choice of material may be determined by considerations regarding the design of the rest of the building, structural strength, ease of maintenance, cost, durability and so on. Opacity is not essential, as some transparency can help more-evenly distribute light.
To be able to reflect light up to the ceiling, the upper surface of light shelves should be matte white or diffusely specular, it does not need to be shiny or reflective. Ideally, the ceiling should also be a light colour.
Light shelves can:
- Enhance daylight quality.
- Reduce the need for artificial lighting and so reduce energy consumption.
- Reduce cooling loads.
- Increase occupant comfort and productivity.
- Enhance design aesthetics.
Some of the limitations or drawbacks of light shelves are as follows:
- They tend to be best-suited to mild rather than tropical or desert climates.
- They can interfere with the installation of sprinkler systems.
- They may require a higher floor-to-ceiling height.
- Their design must be coordinated with windows.
- They Increase maintenance requirements.
Alternative solutions to light shelves include the use of blinds and louvre window systems!
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Retired firefighter cycles world to raise Grenfell funds
Leaving on 14 June 2025 Stephen will raise money for youth and schools through the Grenfell Foundation.
Key points for construction at a glance with industry reactions.
Functionality, visibility and sustainability
The simpler approach to specification.
Architects, architecture, buildings, and inspiration in film
The close ties between makers and the movies, with our long list of suggested viewing.
SELECT three-point plan for action issued to MSPs
Call for Scottish regulation, green skills and recognition of electrotechnical industry as part of a manifesto for Scottish Parliamentary elections.
UCEM becomes the University of the Built Environment
Major milestone in its 106-year history, follows recent merger with London School of Architecture (LSE).
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
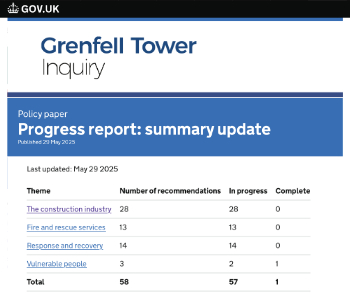
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.