Power float
A power float is a hand-operated machine used to produce a smooth, dense and level surface finish to insitu concrete beds. Power floating eliminates the time and materials needed to apply a finishing screed and is quicker and less labour-intensive process than hand trowelling.
Power floats have an electric motor or petrol engine fixed over a circular pan or skimmer which smooths concrete before hardened steel reversible metal blades rotate at up to 150 rpm over the surface to create a hardened finish.
Before power floating the concrete must be left to partially set, having been leveled and tamped. The amount of setting time necessary before power floating will depend on variables such as; air temperature, humidity, the specification of the mix and so on. A rough guide for considering when to begin power floating is when walking on the surface leaves indentations of 3-4 mm. If the concrete is too wet the machine will tear up the surface, and if it is too dry, it will not be possible to trim high spots or fill low spots effectively.
Floating usually starts at one end of the slab and moves to the other. The operator holds the float at waist-height and moves backwards so that the float removes their footprints. The speed should be slow and consistent.
Once the surface has been floated, the blades are angled to suit the concrete and achieve the specified finish. Blade angles of around 5-10 degrees are usual, but these may need to be increased after each pass over the surface.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Breaker.
- Cement.
- Compressed air plant.
- Concrete.
- Concrete vs. steel.
- Concreting plant.
- Laser screed.
- Screed.
- Tremie.
- Types of floor.
- Types of flooring.
[edit] External references
- Speedcrete - Power floating tips
- ‘Building Construction Handbook’ (6th ed.), CHUDLEY, R., GREENO, R., Butterworth-Heinemann (2007)
Featured articles and news
Guidance notes to prepare for April ERA changes
From the Electrical Contractors' Association Employee Relations team.
Significant changes to be seen from the new ERA in 2026 and 2027, starting on 6 April 2026.
First aid in the modern workplace with St John Ambulance.
Ireland's National Residential Retrofit Plan
Staged initiatives introduced step by step.
Solar panels, pitched roofs and risk of fire spread
60% increase in solar panel fires prompts tests and installation warnings.
Modernising heat networks with Heat interface unit
Why HIUs hold the key to efficiency upgrades.
Reflecting on the work of the CIOB Academy
Looking back on 2025 and where it's going next.
Procurement in construction: Knowledge hub
Brief, overview, key articles and over 1000 more covering procurement.
Sir John Betjeman’s love of Victorian church architecture.
Exchange for Change for UK deposit return scheme
The UK Deposit Management Organisation established to deliver Deposit Return Scheme unveils trading name.
A guide to integrating heat pumps
As the Future Homes Standard approaches Future Homes Hub publishes hints and tips for Architects and Architectural Technologists.
BSR as a standalone body; statements, key roles, context
Statements from key figures in key and changing roles.
ECA launches Welsh Election Manifesto
ECA calls on political parties at 100 day milestone to the Senedd elections.
Resident engagement as the key to successful retrofits
Retrofit is about people, not just buildings, from early starts to beyond handover.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
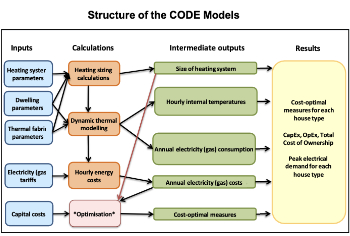
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.