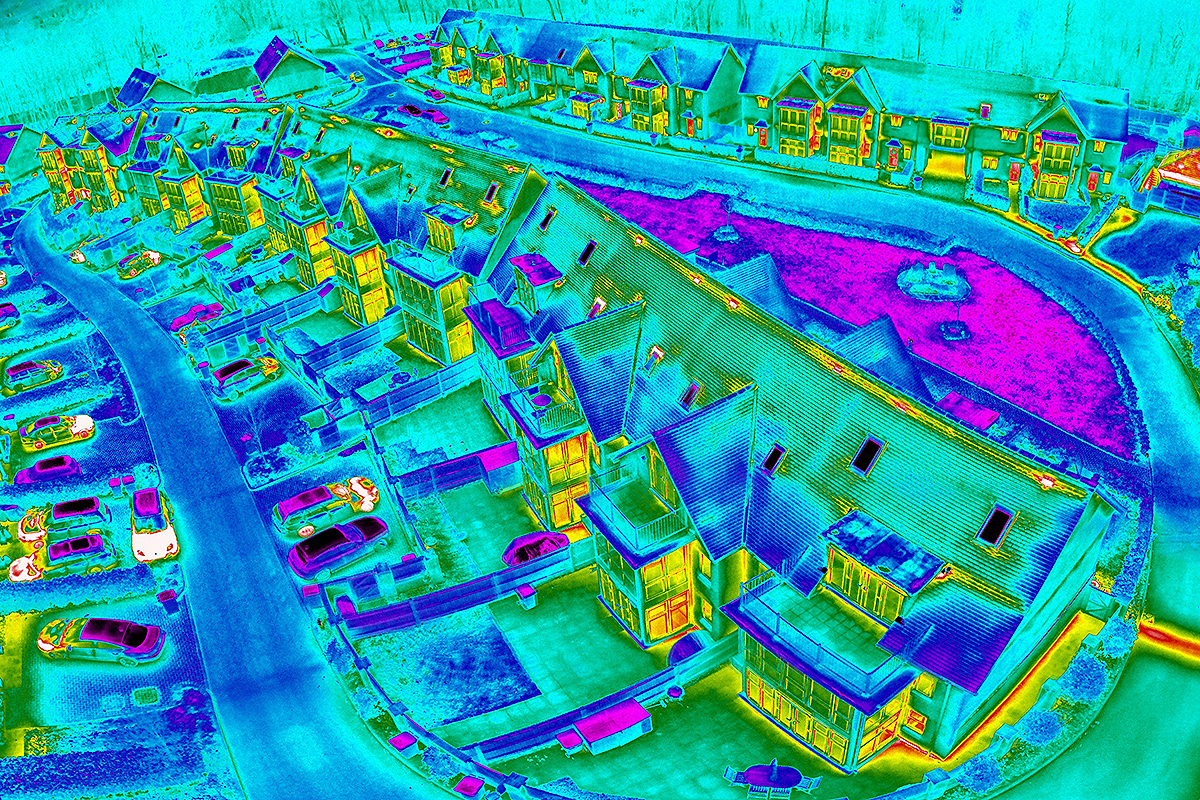
Achieving sustainable futures with thermal imaging
In 2021, the UK Government was the first major economy to pass a net zero emissions law, with a commitment to reduce all greenhouse gas emissions to net zero by 2050. A major part of this is to be achieved through improvements in energy consumption within the built environment.
The energy used to heat the spaces we live and work in is one of the highest contributors to our individual carbon footprints. Globally, heat accounts for nearly half of all energy consumption and 40% of energy-related carbon dioxide emissions.
The carbon footprint of heating, however, is only one half of the story. In order to create a sustainable future, our homes and buildings need to be heated efficiently. This means trapping in the heat we generate instead of allowing it to leak out.
Whilst considerable efforts have been made towards constructing thermally efficient buildings (along with retrofitting older building stock), there is still no mechanism to provide verifiable evidence as to the actual performance of a building. Far too often there are discrepancies between what’s been designed and what’s been built, in turn creating large performance gaps through all stages of the building life cycle.
Thermal imaging is a technique that uses heat-sensitive cameras to detect subtle differences in temperature and is a non-destructive method for assessing heat loss in residential and commercial buildings. As an inspection tool, thermal imaging is able to accurately pinpoint areas for improvement as well as being able to monitor the effectiveness of any remedial works.
Despite numerous initiatives attempting to reduce energy consumption, energy use in buildings has grown continuously over the past 20 years. In order to achieve a net zero economy, it’s now paramount that innovative technologies such as thermal imaging are employed on a global scale to ensure decarbonisation by 2050.
Achieving a sustainable future means developing and retrofitting buildings to meet the needs of today, without compromising the needs of the future. With the global thermal imaging market expected to reach £11.3 billion by 2026 (Global Market Insights, 2019), iRed® is proud to be at the forefront of industry, pioneering new techniques for innovative technologies in an effort to revolutionise the inspection industry and move the global economy to net zero emissions.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.