Self-healing concrete and sweaty roofs: is this the future of buildings?
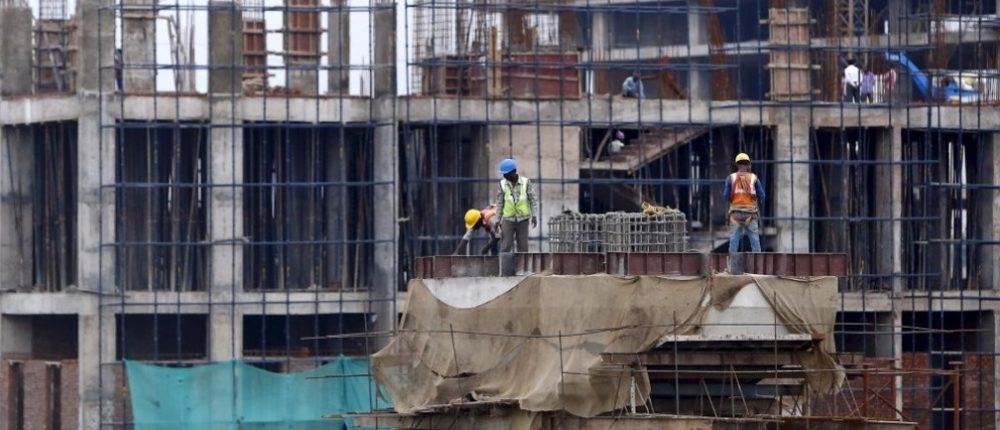
Concrete that can fix itself, roofing that can sweat and surfaces inspired by carnivorous plants are some of the radical new technologies that hold the key to transforming the building industry, according to a new report.
The study, from the World Economic Forum, looks at how the building industry can adapt to some of the key challenges of the next few decades; from meeting the demands of rapid urbanisation to tackling climate change. Shaping the Future of Construction says that an industry which has been traditionally slow to adopt to technology must now move to embrace it.
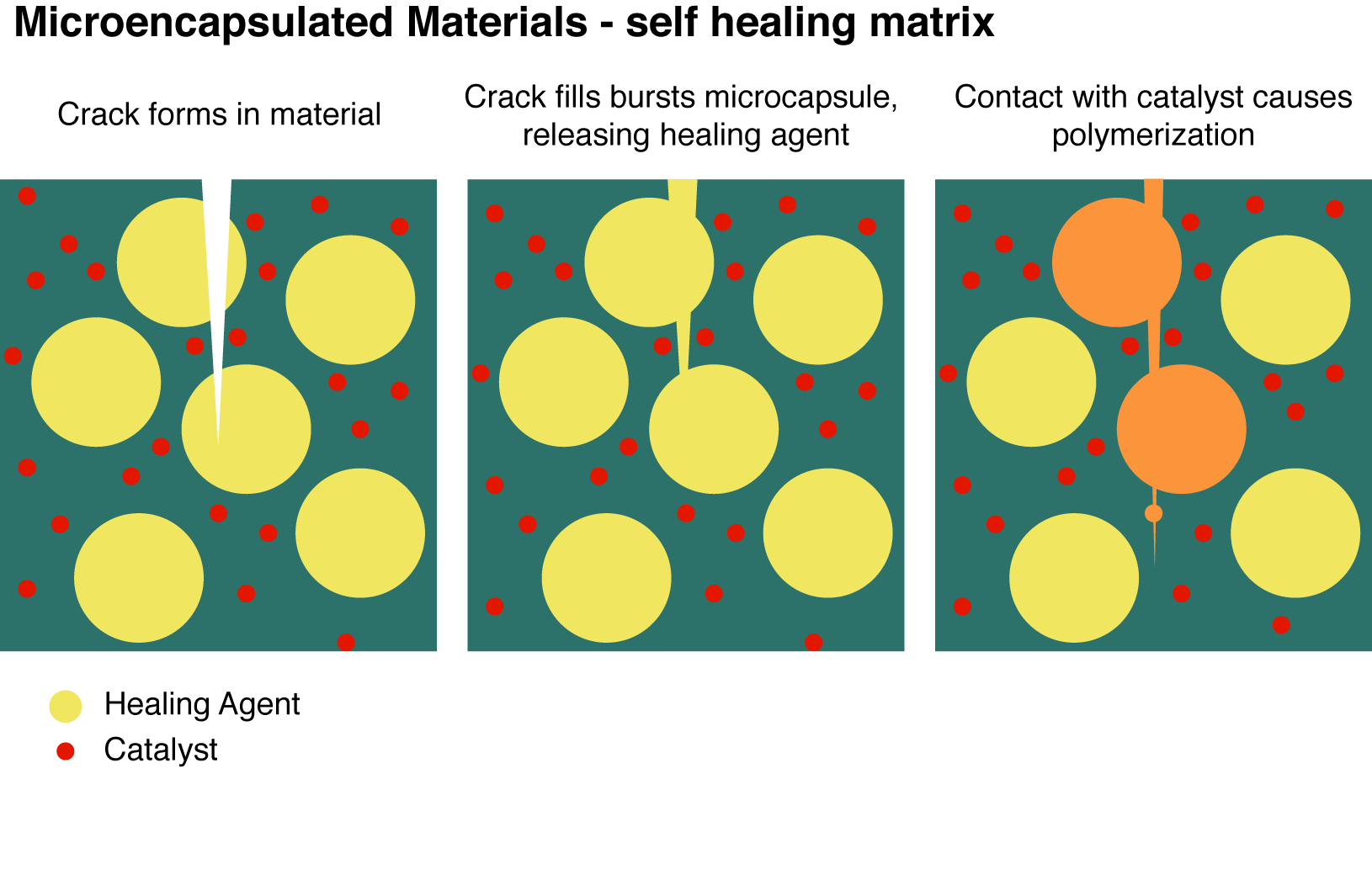
Self-healing concrete is one example of the kind of technology which could add years to a building’s life. The material is able to release a healing agent when cracks appear. When the agent comes into contact with a catalyst inside the concrete it turns into a solid, strong polymer.
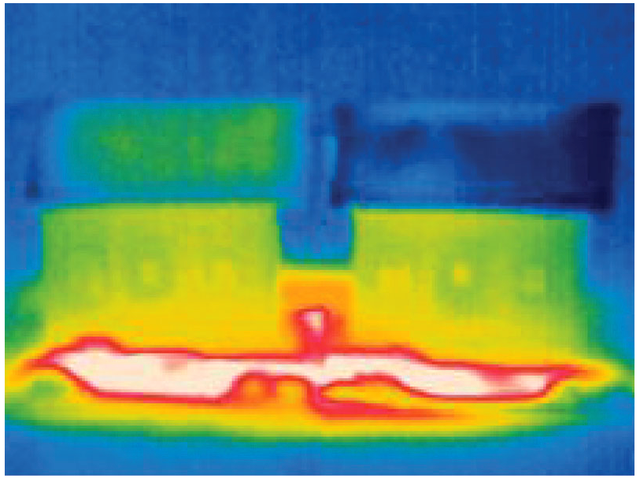
 Another innovation which could significantly reduce running costs is a rain-absorbing matting which, acting in the same way as perspiration, cools the building as the rain evaporates.
Another innovation which could significantly reduce running costs is a rain-absorbing matting which, acting in the same way as perspiration, cools the building as the rain evaporates.
The building on the right of this picture uses the new technology – the infrared image shows the whole structure is cooler than its neighbour.
[Image: Rotzetter ACC/Advanced Materials]
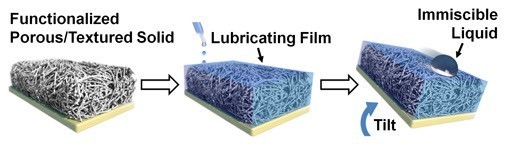
And technology can now mimic a tropical carnivorous plant, the nepenthes, to make surfaces so slippery that they become self-cleaning. The plant uses a slippery surface so that its prey slides inside to be devoured.
Buildings can borrow the same technique for different ends, using a lubricating film makes their surface immiscible to liquid – incapable to mixing with it.
[Image: Wong Laboratory for Nature Inspired Engineering]
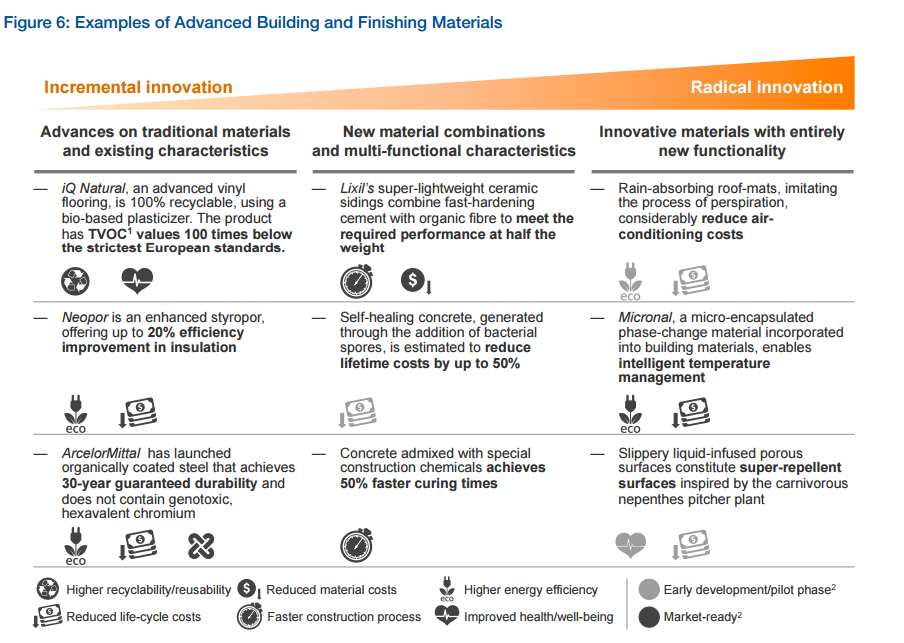
These are just some of the technologies which the report identifies as having the potential to modernise the construction industry – some more radical than others.
[Image: Ellen MacArthur Foundation; World Economic Forum; Boston Consulting Group]
What really needs to change, the report says, is not so much the pace of new technology as the construction industry’s attitude towards it.
Many practices in the construction industry have not substantially changed in 50 years. Traditional, proven methods and materials are used and builders are often focused on the short-term construction costs rather than the lifetime costs of a project. To reduce waste and increase efficiency, that needs to change.
As an industry that strongly affects the economy, the environment and society as a whole and is the world’s largest consumer of raw materials, the construction industry has a key role to play, according to the report’s authors.
There have already been some exceptionally promising developments and there will be many more. Now we need to start using them.
Read the full report, Shaping the Future of Construction: A Breakthrough in Mindset and Technology.
Written by Keith Breene, Formative Content, World Economic Forum
This article was also published on the Future of Construction Knowledge Sharing Platform and the WEF Agenda Blog.
--Future of Construction 09:37, 19 Jun 2017 (BST)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.