About Soorajc899
Technical report writing is a specialized skill essential in fields like engineering and science.
In the professional world, the ability to produce clear, concise, and well-organized technical reports is a critical skill. Technical reports serve as a means of communicating complex information, research findings, and recommendations to a variety of audiences. As such, technical report writing training has become an essential component of professional development for individuals across various industries. This article explores the importance of technical report writing training and provides an overview of key elements that should be included in an effective training program.
Why Technical Report Writing Skills Matter
Technical reports are a cornerstone of decision-making processes in many fields, including engineering, science, information technology, and business. High-quality technical reports can influence project outcomes, drive strategic decisions, and showcase professional expertise. Technical Report Writing Training. Here’s why technical report writing skills are crucial:
- Clear Communication: Technical reports must convey complex technical information in a way that is easily understandable. Effective communication ensures that stakeholders, including managers, clients, and team members, can grasp the findings and implications of the report.
- Professional Credibility: Well-written technical reports reflect a writer’s attention to detail and professionalism. Clear, accurate, and well-structured reports help establish credibility and trust with clients, colleagues, and supervisors.
- Documentation of Findings: Technical reports document research methods, findings, and conclusions. This documentation is essential for historical records, future reference, and ensuring that information is available for review and replication.
- Supporting Decision-Making: Technical reports provide the information needed for informed decision-making. Well-organized reports present data, analyses, and recommendations in a manner that facilitates decision-making processes.
- Compliance and Standards: Many industries require adherence to specific reporting standards and guidelines. Technical report writing training helps professionals understand and comply with these requirements, ensuring reports meet regulatory and organizational standards.
Key Components of Technical Report Writing Training
An effective technical report writing training program should cover several essential components. These components ensure that participants develop the skills necessary to produce high-quality technical reports.
Understanding the Purpose of Technical Reports
The first step in technical report writing training is to help participants understand the different types of technical reports and their purposes. This includes differentiating between research reports, project reports, feasibility studies, and technical specifications. Training should cover:
- Types of Technical Reports: Research reports, progress reports, case studies, and manuals.
- Objectives: Communicating findings, documenting processes, and making recommendations.
Report Structure and Organization
A well-structured report is easier to read and understand. Training should emphasize the standard structure of technical reports, which typically includes:
- Title Page: Report title, author’s name, and date.
- Abstract: A brief summary of the report’s objectives, methods, results, and conclusions.
- Introduction: Background information, objectives, and scope of the report.
- Methods: Detailed description of the methodologies used for research or analysis.
- Results: Presentation of findings, including data, charts, and graphs.
- Discussion: Interpretation of results, implications, and recommendations.
- Conclusion: Summary of findings and final thoughts.
- References: Citations of sources used in the report.
- Appendices: Supplementary material, such as raw data or technical specifications.
Technical Writing Techniques
Training should cover specific techniques for effective technical writing, including:
- Clarity and Precision: Techniques for writing clearly and avoiding jargon or ambiguous language.
- Conciseness: Strategies for conveying information succinctly without sacrificing completeness.
- Logical Flow: Organizing information in a logical sequence that guides the reader through the report.
- Technical Accuracy: Ensuring that technical information is correct and supported by evidence.
Visual Communication
Visual elements such as charts, graphs, and tables are integral to technical reports. Training should include:
- Creating Effective Visuals: Guidelines for designing clear and informative graphs, charts, and tables.
- Integrating Visuals: Best practices for incorporating visuals into the report to support text and clarify information.
Review and Revision Processes
Writing a technical report is not a one-time task but involves multiple stages of review and revision. Training should address:
- Proofreading Techniques: Identifying and correcting errors in grammar, spelling, and formatting.
- Peer Review: The importance of obtaining feedback from colleagues and experts.
- Revising for Improvement: Strategies for revising drafts to enhance clarity, accuracy, and effectiveness.
Compliance with Standards and Guidelines
Training should emphasize the importance of adhering to industry standards and guidelines, such as those set by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) or specific organizational requirements. This includes:
- Familiarity with Standards: Understanding relevant reporting standards and guidelines.
- Applying Standards: Ensuring that reports meet regulatory and organizational requirements.
Implementing a Technical Report Writing Training Program
To implement a successful technical report writing training program, organizations should follow these steps:
- Assess Training Needs: Identify the specific needs of employees through surveys, assessments, or feedback from previous reports.
- Design a Comprehensive Program: Develop a training curriculum that covers the key components outlined above, tailored to the needs of the participants.
- Engage Experienced Trainers: Utilize trainers with expertise in technical writing and industry-specific knowledge.
- Promote Participation: Encourage employees to participate by highlighting the benefits of improved report writing skills for their careers and professional growth.
- Evaluate Effectiveness: Gather feedback from participants and assess improvements in report quality to refine and enhance the training program.
Featured articles and news
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
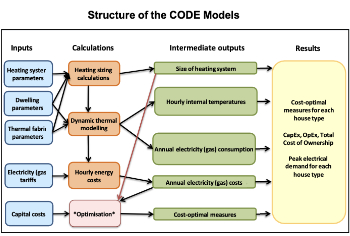
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.