About Omarmanshi
Student Architecture part 1.
By adding a layer of heat sensitive stripe-type-lambda-trititanium-pentoxide, is composed of only titanium atoms and oxygen atoms, and can absorb and release a large amount of heat. This material, called stripe-type-lambda-trititanium-pentoxide, is composed of only titanium atoms and oxygen atoms, and can absorb and release a large amount of heat energy (230 kJ L1). This heat energy stored is large at approximately 70% of the latent heat energy of water at its melting point. Additionally, applying a weak pressure of 60 MPa (mega Pascal) to stripe-type-lambda-trititanium-pentoxide induces a phase transition to beta-trititanium-pentoxide, releasing the stored heat energy. Besides direct application of heat, heat energy can be stored by passing an electric current through the material or irradiating it with light, enabling the repeated absorption and release of heat energy by a variety of methods
Applying this new development in energy efficient material to a layer of thermal bimetal (to sheets of metal, copper and steel attached to one another with different rates of expansion in response to heat) will allow for the a south facing façade during hot weather periods to expand and cover the façade providing natural shading throughout the day whilst absorbing and storing heat and be able to redistribute it throughout the day towards the north facing façade where sunlight is not directly reaching and throughout the night or during colder periods of time during the year. The properties of the bimetal will be able to allow for openings to be made in order to provide an energy efficient means of ventilating a building whilst at the same time using the stripe-type-lambda-trititanium-pentoxide to store heat for when needed. The redistribution of the heat energy stored using this method may not have to be random either By using an integrating advance system linked to a smart metering used to control ambient temperature in domestic and commercial buildings would allow for the redistribution of heat energy to be controlled and manipulated. This idea could even be extended on a larger scale to have all the controlled managed by a larger system connecting all the stored energy and dispense it according to when needed.
Featured articles and news
Editor's broadbrush view on forms of electrical heating in context.
The pace of heating change; BSRIA market intelligence
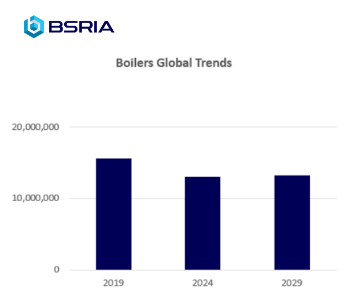
Electric Dreams, Boiler Realities.
New President of ECA announced
Ruth Devine MBE becomes the 112th President of the Electrical Contractors Association.
New CIAT Professional Standards Competency Framework
Supercedes the 2019 Professional Standards Framework from 1 May 2025.
Difficult Sites: Architecture Against the Odds
Free exhibition at the RIBA Architecture Gallery until 31 May.
PPN 021: Payment Spot Checks in Public Sub-Contracts
Published following consultation and influence from ECA.
Designing Buildings reaches 20,000 articles
We take a look back at some of the stranger contributions.
Lessons learned from other industries.
The Buildings of the Malting Industry. Book review.
Conserving places with climate resilience in mind.
Combating burnout.
The 5 elements of seiri, seiton, seiso, seiketsu and shitsuke.
Shading for housing, a design guide
A look back at embedding a new culture of shading.
The Architectural Technology Awards
The AT Awards 2025 are open for entries!
ECA Blueprint for Electrification
The 'mosaic of interconnected challenges' and how to deliver the UK’s Transition to Clean Power.
Grenfell Tower Principal Contractor Award notice
Tower repair and maintenance contractor announced as demolition contractor.