Reverberation in buildings
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Sound is caused by vibrations which transmit through a medium such as air and reach the ear or some other form of detecting device. Sound intensity is measured in Decibels (dB). This is a logarithmic scale in which an increase of 10 dB gives an apparent doubling of loudness.
Approved document E, Resistance to the passage of sound defines 'Reverberation' as the persistence of sound in a space after a sound source has been stopped. Reverberation time is the time, in seconds, taken for the sound to decay by 60dB after a sound source has been stopped.
The reverberation time of a room is linked to the the surfaces that enclose it and the volume of the room by the Sabine equation:
RT = Volume x 0.161 / Total Acoustic Absorption
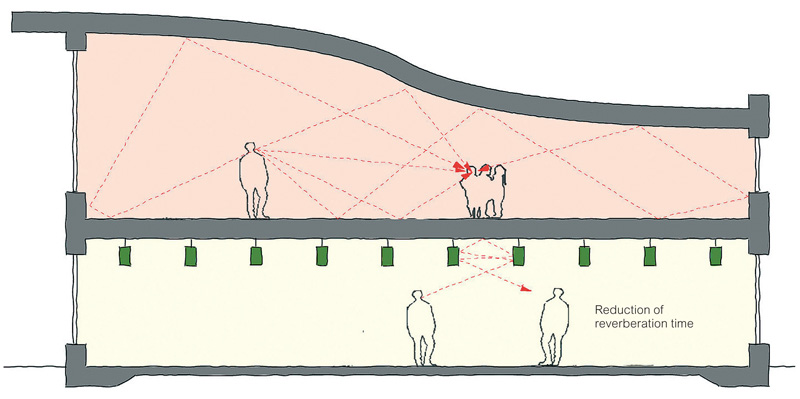
Image: To control reverberation time, acoustic absorption is used.
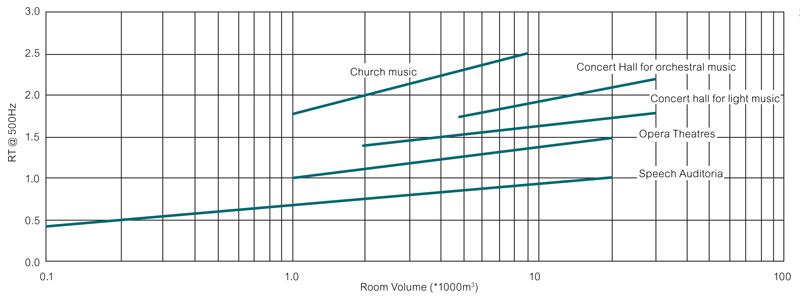
Room acoustics / reverberation affects the way a space sounds. A high reverberation time can make a room sound loud and noisy. Speech intelligibility is also a function of reverberation, a high reverberation time causes speech to sound muffled and muddy. Rooms designed for speech therefore typically have a low reverberation time: ≤1 second. A high reverberation time can enhance a music hall by adding richness, depth and warmth to music. A higher level of reverberation within a concert hall is therefore critical.
The illustration below provides indicative reverberation times for a range of building types and room volumes.
[edit] Acoustic properties of materials
To control reverberation time, acoustic absorption is used. Absorbent materials conventionally take two forms; fibrous materials or open-celled foam. Fibrous materials absorb sound as sound waves force the fibres to bend and this bending of the fibres generates heat. The conversion of acoustic energy into heat energy results in the sound effectively being absorbed. In the case of open-celled foam, the air movement resulting from sound waves pushes air particles through the narrow passages which in turn generate a viscous loss along with heat.
Architecturally, fibrous materials and open celled foams are not always considered attractive or robust. It is common therefore to cover these materials with an acoustically transparent finish such as a tissue, cloth or slatted wood, or with perforated materials such as wood, metal, plasterboard and so on.
The thickness of a given material along with properties such as its fibrousity governs its acoustic performance. Finishes within a space are defined in terms of their absorption coefficient. This is a number between 0.0 (100% reflective) for example stone, tiles or concrete and 1.0 (100% absorbent), for example high performance acoustic ceiling tiles, slabs of mineral wool, etc. Products such as carpets typically have an absorption coefficient between 0.1 and 0.3 depending on their thickness. Perforated plasterboard generally provides around 0.6 to 0.7.
It is also common to classify absorbent materials in categories, A to E, where A is highly absorbent and E is almost fully reflective.
This article was created by --MACH Acoustics 11:04, 28 November 2013 (UTC)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Airborne sound.
- Approved Document E.
- Building acoustics.
- Building Bulletin 93: acoustic design of schools.
- Decibel.
- Flanking sound.
- Impact sound.
- Noise nuisance.
- Robust details certification scheme.
- Room acoustics.
- Sound insulation.
- Sound absorption.
- Sound frequency.
- Sound insulation testing.
- Sound power.
- Sound v noise.
- Noise nuisance.
[edit] External references
- MACH Acoustics: Room acoustics and reverberation.
Featured articles and news
RTPI leader to become new CIOB Chief Executive Officer
Dr Victoria Hills MRTPI, FICE to take over after Caroline Gumble’s departure.
Social and affordable housing, a long term plan for delivery
The “Delivering a Decade of Renewal for Social and Affordable Housing” strategy sets out future path.
A change to adoptive architecture
Effects of global weather warming on architectural detailing, material choice and human interaction.
The proposed publicly owned and backed subsidiary of Homes England, to facilitate new homes.
How big is the problem and what can we do to mitigate the effects?
Overheating guidance and tools for building designers
A number of cool guides to help with the heat.
The UK's Modern Industrial Strategy: A 10 year plan
Previous consultation criticism, current key elements and general support with some persisting reservations.
Building Safety Regulator reforms
New roles, new staff and a new fast track service pave the way for a single construction regulator.
Architectural Technologist CPDs and Communications
CIAT CPD… and how you can do it!
Cooling centres and cool spaces
Managing extreme heat in cities by directing the public to places for heat stress relief and water sources.
Winter gardens: A brief history and warm variations
Extending the season with glass in different forms and terms.
Restoring Great Yarmouth's Winter Gardens
Transforming one of the least sustainable constructions imaginable.
Construction Skills Mission Board launch sector drive
Newly formed government and industry collaboration set strategy for recruiting an additional 100,000 construction workers a year.
New Architects Code comes into effect in September 2025
ARB Architects Code of Conduct and Practice available with ongoing consultation regarding guidance.
Welsh Skills Body (Medr) launches ambitious plan
The new skills body brings together funding and regulation of tertiary education and research for the devolved nation.
Paul Gandy FCIOB announced as next CIOB President
Former Tilbury Douglas CEO takes helm.
UK Infrastructure: A 10 Year Strategy. In brief with reactions
With the National Infrastructure and Service Transformation Authority (NISTA).